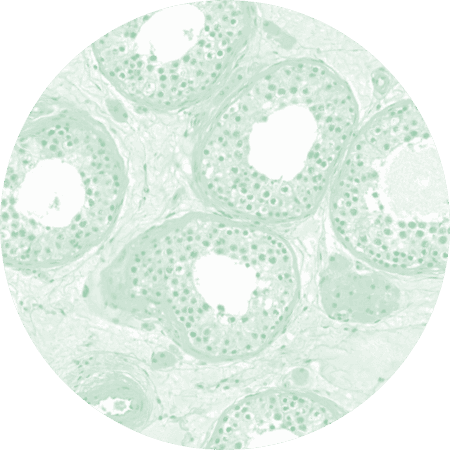
A chondrocyte (also known by the name of cartilage cell) is a cell originating from chondroblasts and located in cartilaginous tissue. Chondrocytes produce the extracellular matrix of cartilaginous tissue. Their high synthetic performance is attributable to an advanced Golgi apparatus and plenty of rough endoplasmic reticulum. Their cellular structure is maintained by vimentin filaments of reticular arrangement within the cytoplasm. Chondrocytes are singularly scattered in cartilage cavities, with cartilage height being delimited from surrounding tissue by collagen fibres (Type II). Blood supply to chondrocytes is through the perichondrium and synovial fluid. In regenerative medicine, chondrocyte cultures are fixed on carrier material and are used for regeneration of cartilage.